Difference between revisions of "AR488"
(images for AR488 and LCSoft combination) |
("discuss" sniffing the AR488's GPIB communication) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
File:ar488-lcsoft-stack-side.png|<small>AR488 and LCSoft Mini, side view</small> | File:ar488-lcsoft-stack-side.png|<small>AR488 and LCSoft Mini, side view</small> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
While the immediate effect of building an AR488 is to have a GPIB adapter to talk to measurement gear, a side effect could be the opportunity to capture the wire communication while the devices are talking. This can support the analysis of communication issues, as well as can help during development of support for other devices. | |||
== Protocol == | == Protocol == | ||
Latest revision as of 07:13, 10 October 2023
AR488 GPIB to UART/USB
The AR488 is an Arduino-based GPIB to serial port adapter. The firmware runs on Uno (and thus Nano), Mega as well as Leonardo boards. The PC sees a USB or RS-232 attached COM port, transmit data is sent to the device, and the device's response is seen as receive data. Out-of-band commands prefixed by ++ can control the adapter's behaviour. The AR488 is accessible to interactive sessions in a terminal program, as well as can serve as a SCPI-over-serial "cable".
With one device per adapter (specific GPIB address and communication parameters stored in the AR488 adapter) support is transparent. When the adapter is connected to multiple devices at the same time, then "out-of-band" communication is required (the above mentioned ++ commands), which sigrok does not provide.
Hardware
- Arduino Uno or Nano (ATmega328P based), or Mega (ATmega2560 based), or Leonardo or Pro Micro (ATmega32U4 based)
- Centronics 24-pin connector
See the AR488-manual.pdf in the firmware source tree for schematics. Wires run from the Arduino board to the Centronics connector, and driver chips are not involved. This keeps the component count low, the wiring simple, and the mechanical construction compact (especially with Nano boards which can execute the Uno firmware). In theory, any bare serially attached ATmega chip would do, but the firmware happens to be written in the Arduino IDE's language (it uses libraries and build support, and won't work outside of the IDE without modifications).
The primary goal of the project is to enable quick access to GPIB attached devices. Typical use is to have one adapter per device (it's rather low cost, so that's not an issue). The lack of proper drivers means that the adapter cannot handle a full bus. The limit is said to be somewhere around three or four devices, before signals go out of spec and communication need not work reliably any longer. For larger setups with many devices, a proper full-blown adapter with appropriate driving capabilities is recommended.
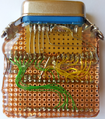
Photos
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
LCSoft Mini riser board for AR488
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
AR488 and LCSoft Mini, top view
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
AR488 and LCSoft Mini, side view
While the immediate effect of building an AR488 is to have a GPIB adapter to talk to measurement gear, a side effect could be the opportunity to capture the wire communication while the devices are talking. This can support the analysis of communication issues, as well as can help during development of support for other devices.
Protocol
See the AR488-manual.pdf document for a protocol description. The AR488 firmware passes the PC's outgoing data to the GPIB instrument, and the GPIB instrument's data to the PC. Commands start with the ++ prefix and affect the adapter's operation. The AR488 firmware implements most of the Prologix commands, and a few more. Macros (both executed at runtime as well as at firmware start) are supported.
How to use the AR488 adapter:
- (Optional, see below) Modify the firmware to enable the macro feature and especially the startup macro (remove comment leaders from disabled defines).
#define MACROS #define STARTUP
- (Optional, see below) Locate the startup_macro[] definition and adjust it to match your use case. Here is an example.
++addr 20 ++auto 2
- (Optional, see below) Compile and upload the firmware into the adapter.
- (See above for custom firmware) Regular common firmware can interactively get configured and that configuration can get stored in the adapter. Which eliminates the necessity for custom builds, and ++ commands at the start of a session. See the AR488 manual which parameter values get stored and applied upon firmware startup.
++ addr 20 ++ auto 2 ++ savecfg ++ rst
- Open a terminal program and run a few commands.
$ screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200 *idn? conf? read? ++repeat 15 4000 read?
- Use the adapter with GPIB aware applications, like sigrok's SCPI over serial.
$ sigrok-cli -d scpi-dmm:conn=/dev/ttyUSB0:serialcomm=115200 --scan
- Alternative mix of interactive and programmatic use.
$ screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200 ++ addr 22 ++ auto 2 (close terminal session) $ sigrok-cli -d scpi-dmm:conn=/dev/ttyUSB0:serialcomm=115200
BEWARE! Depending on the specific implementation of the Arduino board, the adapter may restart when the serial port gets opened, and the volatile configuration may not take effect at all. This is an implementation detail of deriving a RESET signal from the DTR handshake, motivated by automatically entering bootloaders without the user's intervention. Consider the ++savecfg approach outlined above instead.
Resources
- Twilight Logic's GitHub repo, contains firmware sources and documentation
- EEVBlog forum thread