Difference between revisions of "Protocol decoder:Ook vis"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
It is provided to help analyse unknown format waveforms. Using the ook decoder with this one allows you to try '''NRZ''', '''Manchester''' and '''Differential Manchester''' and their possible settings to see what produces the lowest errors. Then use ook_vis to format the results in a suitable fashion for what you are decoding, make some structure assumptions and see what that does to the results. | It is provided to help analyse unknown format waveforms. Using the ook decoder with this one allows you to try '''NRZ''', '''Manchester''' and '''Differential Manchester''' and their possible settings to see what produces the lowest errors. Then use ook_vis to format the results in a suitable fashion for what you are decoding, make some structure assumptions and see what that does to the results. | ||
The '''ook_vis''' protocol decoder provides two lines of decode. The first line does a basic decode (with formatting) while the second attempts to work out where the preamble and sync might be and then displays the data with a posible structure. The sync position is worked out from the preamble and detects when it switches from '1111 | The '''ook_vis''' protocol decoder provides two lines of decode. The first line does a basic decode (with formatting) while the second attempts to work out where the preamble and sync might be and then displays the data with a posible structure. The sync position is worked out from the preamble and detects when it switches from '1111' or '1010' to something else. | ||
== Decoder == | == Decoder == | ||
The '''ook_vis''' decoder has | The '''ook_vis''' decoder has four options | ||
{'id': 'displayas', 'desc': 'Display as', 'default': 'Nibble - Hex', 'values': ('Byte - Hex','Byte - Hex rev', 'Byte - BCD','Byte - BCD rev','Nibble - Hex','Nibble - Hex rev','Nibble - BCD','Nibble - BCD rev',)}, | {'id': 'displayas', 'desc': 'Display as', 'default': 'Nibble - Hex', 'values': ('Byte - Hex','Byte - Hex rev', 'Byte - BCD','Byte - BCD rev','Nibble - Hex','Nibble - Hex rev','Nibble - BCD','Nibble - BCD rev',)}, | ||
{'id': 'synclen', 'desc': 'Sync length', 'default': '4', 'values': ('0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10')}, | {'id': 'synclen', 'desc': 'Sync length', 'default': '4', 'values': ('0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10')}, | ||
{'id': 'syncoffset', 'desc': 'Sync | {'id': 'syncoffset', 'desc': 'Sync offset', 'default': '0', 'values': ('-4','-3','-2','-1','0','1','2','3','4')} | ||
{'id': 'refsample', 'desc': 'Compare', 'default': 'off', 'values': ('off', 'show numbers', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11', '12', '13', '14', '15', '16', '17', '18', '19', '20', '21', '22', '23', '24', '25', '26', '27', '28', '29', '30')} | |||
The '''displayas''' option allows the user to pick how the data is presented. It | The '''displayas''' option allows the user to pick how the data is presented. It supports two lengths 4 bits (Nibble) and 8 bits (Byte). It also allows numbers to be displayed as Hexadecimal or Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) and also supports bit reversal. | ||
The '''synclen''' option allows the user to set the length of the Sync and vary it to see what that does to the data after it. | The '''synclen''' option allows the user to set the length of the Sync and vary it to see what that does to the data after it. | ||
The '''syncoffset''' option allows the user to move the start of sync backwards and forwards to see what that does to the data after it. | The '''syncoffset''' option allows the user to move the start of sync backwards and forwards to see what that does to the data after it. | ||
The '''refsample''' option allows one of the packets to be used as a reference sample which all the packets are compared against. To use this feature first select '''show numbers''' to identify which packet to use, then select the packet number from 1 - 30. To turn it off again select off. | |||
You can show the available options with the --show command: | You can show the available options with the --show command: | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 24 September 2018
 | |
| Name | OOK Visualiser |
|---|---|
| Description | On Off Keying Visualiser |
| Status | possible candidate |
| License | GPLv2+ |
| Source code | decoders/ook_vis |
| Input | ook |
| Output | ook |
| Probes | none |
| Optional probes | — |
| Options | displayas, synclen, syncoffset |
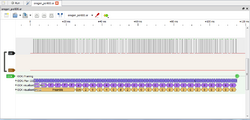
The ook_vis protocol decoder takes ook input from the ook decoder and displays it in a variety of formats.
It is provided to help analyse unknown format waveforms. Using the ook decoder with this one allows you to try NRZ, Manchester and Differential Manchester and their possible settings to see what produces the lowest errors. Then use ook_vis to format the results in a suitable fashion for what you are decoding, make some structure assumptions and see what that does to the results.
The ook_vis protocol decoder provides two lines of decode. The first line does a basic decode (with formatting) while the second attempts to work out where the preamble and sync might be and then displays the data with a posible structure. The sync position is worked out from the preamble and detects when it switches from '1111' or '1010' to something else.
Decoder
The ook_vis decoder has four options
{'id': 'displayas', 'desc': 'Display as', 'default': 'Nibble - Hex', 'values': ('Byte - Hex','Byte - Hex rev', 'Byte - BCD','Byte - BCD rev','Nibble - Hex','Nibble - Hex rev','Nibble - BCD','Nibble - BCD rev',)},
{'id': 'synclen', 'desc': 'Sync length', 'default': '4', 'values': ('0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10')},
{'id': 'syncoffset', 'desc': 'Sync offset', 'default': '0', 'values': ('-4','-3','-2','-1','0','1','2','3','4')}
{'id': 'refsample', 'desc': 'Compare', 'default': 'off', 'values': ('off', 'show numbers', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11', '12', '13', '14', '15', '16', '17', '18', '19', '20', '21', '22', '23', '24', '25', '26', '27', '28', '29', '30')}
The displayas option allows the user to pick how the data is presented. It supports two lengths 4 bits (Nibble) and 8 bits (Byte). It also allows numbers to be displayed as Hexadecimal or Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) and also supports bit reversal.
The synclen option allows the user to set the length of the Sync and vary it to see what that does to the data after it.
The syncoffset option allows the user to move the start of sync backwards and forwards to see what that does to the data after it.
The refsample option allows one of the packets to be used as a reference sample which all the packets are compared against. To use this feature first select show numbers to identify which packet to use, then select the packet number from 1 - 30. To turn it off again select off.
You can show the available options with the --show command:
$ sigrok-cli -P ook_vis --show
sigrok-cli examples
The ook_vis decoder concentrates on the protocol and not how it is transmitted so it needs the ook decoder to deal with the encoding before it can do its work. It stacks on top of the ook decoder.
To decode a Manchester (default) encoded trace with a preamble starting 1111 (default) (Oregon V3 sensor) and then pass the result to the ook_vis decoder and only display the ook_vis output. The trace belongs to a real Oregon v3 rain sensor model PCR800.
sigrok-cli -P ook:data=D0,ook_vis -i oregon_pcr800.sr -A ook_vis