Difference between revisions of "Sigrok-cli"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (30 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:sigrok-cli}} | |||
'''sigrok-cli''' (sometimes abbreviated as "cli") is a command-line frontend for sigrok. | |||
It is licensed under the terms of the '''GNU GPL, version 3 or later'''. | |||
== | == Getting the code == | ||
$ '''git clone git://sigrok.org/sigrok-cli''' | |||
You can also [http://sigrok.org/gitweb/?p=sigrok-cli.git;a=tree browse the source code] via gitweb. | |||
== Distribution packages == | |||
See [[Downloads#Binaries_and_distribution_packages|Downloads]]. | |||
== | == Building from source == | ||
See [[Building]]. | |||
== Usage tips == | |||
It is recommended to capture the data first and process them later. sigrok-cli is single-threaded application and too much load will overwhelm it resulting in early termination. For capturing, use binary output format (especially for high sample-rates). This is because other formats pose too big overhead. | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver saleae-logic-pro --channels 0=Vcc,1=CS,2=MISO,3=MOSI,4=CLK --output-file <file>.bin --output-format binary --config samplerate=50m --continuous | |||
Even better, consider to use a buffer instead of direct write (even on SSD) and also compression. | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver saleae-logic-pro --channels 0=Vcc,1=CS,2=MISO,3=MOSI,4=CLK --output-format binary --config samplerate=50m --continuous | mbuffer | lz4 | pv > data.lz4q | |||
== Manpage == | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" overflow:auto;"> | |||
<!-- Generated by: "LC_ALL=C nroff -man doc/sigrok-cli.1 | col -b". --> | |||
<pre> | |||
SIGROK-CLI(1) General Commands Manual SIGROK-CLI(1) | |||
NAME | |||
sigrok-cli - Command-line client for the sigrok software | |||
SYNOPSIS | |||
sigrok-cli [OPTIONS] [COMMAND] | |||
DESCRIPTION | |||
sigrok-cli is a cross-platform command line utility for the sigrok | |||
software. | |||
It cannot display graphical output, but is still sufficient to run | |||
through the whole process of hardware initialization, acquisition, pro- | |||
tocol decoding and saving the session. | |||
It is useful for running on remote or embedded systems, netbooks, PDAs, | |||
and for various other use-cases. It can display samples on standard | |||
output or save them in various file formats. | |||
OPTIONS | |||
-h, --help | |||
Show a help text and exit. | |||
-V, --version | |||
Show sigrok-cli version and the versions of libraries used. | |||
1:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 | -L, --list-supported | ||
Show information about supported hardware drivers, input file | |||
formats, output file formats, and protocol decoders. | |||
-d, --driver <drivername> | |||
A driver must always be selected (unless doing a global scan). | |||
Use the -L (--list-supported) option to get a list of available | |||
drivers. | |||
Drivers can take options, in the form key=value separated by | |||
colons. | |||
Drivers communicating with hardware via a serial port always | |||
need the port specified as the conn option. For example, to use | |||
the Openbench Logic Sniffer: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver=ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 [...] | |||
Some USB devices don't use a unique VendorID/ProductID combina- | |||
tion, and thus need that specified as well. This also uses the | |||
conn option, using either VendorID.ProductID or bus.address: | |||
USB VendorID.ProductID example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver=uni-t-ut61e:conn=1a86.e008 [...] | |||
USB bus.address example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver=uni-t-ut61e:conn=4.6 [...] | |||
-c, --config <deviceoption> | |||
A colon-separated list of device options, where each option | |||
takes the form key=value. For example, to set the samplerate to | |||
1MHz on a device supported by the fx2lafw driver, you might | |||
specify | |||
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1m [...] | |||
Samplerate is an option common to most logic analyzers. The | |||
argument specifies the samplerate in Hz. You can also specify | |||
the samplerate in kHz, MHz or GHz. The following are all equiv- | |||
alent: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1000000 [...] | |||
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1m [...] | |||
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config "samplerate=1 MHz" [...] | |||
-i, --input-file <filename> | |||
Load input from a file instead of a hardware device. You can | |||
specify "-" to use stdin as input. If the --input-format option | |||
is not supplied, sigrok-cli attempts to autodetect the file for- | |||
mat of the input file. | |||
Example for loading a sigrok session file: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i example.sr [...] | |||
Example for loading a WAV file (autodetection of input format): | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i example.wav [...] | |||
Example for loading a VCD file from stdin (autodetection of | |||
input format): | |||
$ cat example.vcd | sigrok-cli -i - [...] | |||
-I, --input-format <format> | |||
When loading an input file, assume it's in the specified format. | |||
If this option is not supplied (in addition to --input-file), | |||
sigrok-cli attempts to autodetect the file format of the input | |||
file. Use the -L (--list-supported) option to see a list of | |||
available input formats. | |||
The format name may optionally be followed by a colon-separated | |||
list of options, where each option takes the form key=value. | |||
Example for loading a binary file with options: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i example.bin | |||
-I binary:numchannels=4:samplerate=1mhz [...] | |||
-o, --output-file <filename> | |||
Save output to a file instead of writing it to stdout. The | |||
default format used when saving is the sigrok session file for- | |||
mat. This can be changed with the --output-format option. | |||
Example for saving data in the sigrok session format: | |||
$ sigrok-cli [...] -o example.sr | |||
-O, --output-format <format> | |||
Set the output format to use. Use the -L (--list-supported) | |||
option to see a list of available output formats. | |||
The format name may optionally be followed by a colon-separated | |||
list of options, where each option takes the form key=value. | |||
For example, the bits or hex formats, for an ASCII bit or ASCII | |||
hexadecimal display, can take a "width" option, specifying the | |||
number of samples (in bits) to display per line. Thus -O | |||
hex:width=128 will display 128 bits per line, in hexadecimal: | |||
0:ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff | |||
1:ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 | |||
The lines always start with the channel number (or name, if | |||
defined), followed by a colon. If no format is specified, it | |||
defaults to bits:width=64, like this: | |||
0:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
1:11111111 00000000 11111111 00000000 [...] | |||
Example for saving data in the CSV format with options: | |||
$ sigrok-cli [...] -o example.csv -O csv:dedup:header=false | |||
Notice that boolean options are true when no value gets speci- | |||
fied. | |||
-C, --channels <channellist> | |||
A comma-separated list of channels to be used in the session. | |||
Note that sigrok always names the channels according to how | |||
they're shown on the enclosure of the hardware. If your logic | |||
analyzer numbers the channels 0-15, that's how you must specify | |||
them with this option. An oscilloscope's channels would gener- | |||
ally be referred to as "CH1", "CH2", and so on. Use the --show | |||
option to see a list of channel names for your device. | |||
The default is to use all the channels available on a device. | |||
You can name a channel like this: 1=CLK. A range of channels | |||
can also be given, in the form 1-5. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --samples 100 | |||
--channels 1=CLK,2-4,7 | |||
CLK:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
2:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
3:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
4:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
7:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...] | |||
The comma-separated list is processed from left to right, i.e. | |||
items farther to the right override previous items. For example | |||
1=CS,CS=MISO will set the name of channel 1 to MISO. | |||
-g, --channel-group <channel group> | |||
Specify the channel group to operate on. Some devices organize | |||
channels into groups, the settings of which can only be changed | |||
as a group. The list of channel groups, if any, is displayed | |||
with the --show command. | |||
Examples: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -g CH1 [...] | |||
$ sigrok-cli -d demo -g Logic -c pattern=graycode [...] | |||
-t, --triggers <triggerlist> | |||
A comma-separated list of triggers to use, of the form <chan- | |||
nel>=<trigger>. You can use the name or number of the channel, | |||
and the trigger itself is a series of characters: | |||
0 or 1: A low or high value on the pin. | |||
r or f: A rising or falling value on the pin. An r effectively | |||
corresponds to 01. | |||
e: Any kind of change on a pin (either a rising or a falling | |||
edge). | |||
Not every device supports all of these trigger types. Use the | |||
--show command to see which triggers your device supports. | |||
-w, --wait-trigger | |||
Don't output any sample data (even if it's actually received | |||
from the hardware) before the trigger condition is met. In other | |||
words, do not output any pre-trigger data. This option is useful | |||
if you don't care about the data that came before the trigger | |||
(but the hardware delivers this data to sigrok nonetheless). | |||
-P, --protocol-decoders <list> | |||
This option allows the user to specify a comma-separated list of | |||
protocol decoders to be used in this session. The decoders are | |||
specified by their ID, as shown in the -L (--list-supported) | |||
output. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c | |||
Each protocol decoder can optionally be followed by a colon-sep- | |||
arated list of options, where each option takes the form | |||
key=value. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> | |||
-P uart:baudrate=115200:parity_type=odd | |||
The list of supported options depends entirely on the protocol | |||
decoder. Every protocol decoder has different options it sup- | |||
ports. | |||
Any "options" specified for a protocol decoder which are not | |||
actually supported options, will be interpreted as being channel | |||
name/number assignments. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> | |||
-P spi:wordsize=9:miso=1:mosi=5:clk=3:cs=0 | |||
In this example, wordsize is an option supported by the spi pro- | |||
tocol decoder. Additionally, the user tells sigrok to decode the | |||
SPI protocol using channel 1 as MISO signal for SPI, channel 5 | |||
as MOSI, channel 3 as CLK, and channel 0 as CS# signal. | |||
Notice that the sigrok-cli application does not support "name | |||
matching". Instead it's assumed that the traces in the input | |||
stream match the order of the decoder's input signals, or that | |||
users explicitly specify the input channel to decoder signal | |||
mapping. | |||
When multiple decoders are specified in the same -P option, they | |||
will be stacked on top of each other in the specified order. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,eeprom24xx | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P uart:baudrate=31250,midi | |||
When multiple -P options are specified, each of them creates one | |||
decoder stack, which executes in parallel to other decoder | |||
stacks. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P uart:tx=D0:rx=D1 -P timing:data=D2 | |||
-A, --protocol-decoder-annotations <annotations> | |||
By default, all annotation output of all protocol decoders is | |||
shown. With this option a specific decoder's annotations can be | |||
selected for display, by specifying the decoder ID: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid -A i2c | |||
If a protocol decoder has multiple annotation classes, you can | |||
also specify which one of them to show by specifying its short | |||
description like this: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid | |||
-A i2c=data-read | |||
Select multiple annotation classes by separating them with a | |||
colon: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid | |||
-A i2c=data-read:data-write | |||
You can also select multiple protocol decoders, with an optional | |||
selected annotation class each, by separating them with commas: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid | |||
-A i2c=data-read:data-write,edid | |||
-M, --protocol-decoder-meta <pdname> | |||
When given, show protocol decoder meta output instead of annota- | |||
tions. The argument is the name of the decoder whose meta out- | |||
put to show. | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -M i2c | |||
Not every decoder generates meta output. | |||
-B, --protocol-decoder-binary <binaryspec> | |||
When given, decoder "raw" data of various kinds is written to | |||
stdout instead of annotations (this could be raw binary UART/SPI | |||
bytes, or WAV files, PCAP files, PNG files, or anything else; | |||
this is entirely dependent on the decoder and what kinds of | |||
binary output make sense for that decoder). | |||
No other information is printed to stdout, so this is suitable | |||
for piping into other programs or saving to a file. | |||
Protocol decoders that support binary output publish a list of | |||
binary classes, for example the UART decoder might have "TX" and | |||
"RX". To select TX for output, the argument to this option would | |||
be: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -B uart=tx | |||
If only the protocol decoder is specified, without binary class, | |||
all classes are written to stdout: | |||
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -B uart | |||
(this is only useful in rare cases, generally you would specify | |||
a certain binary class you're interested in) | |||
Not every decoder generates binary output. | |||
--protocol-decoder-samplenum | |||
When given, decoder annotations will include sample numbers, | |||
too. This allows consumers to receive machine readable timing | |||
information. | |||
-l, --loglevel <level> | |||
Set the libsigrok and libsigrokdecode loglevel. At the moment | |||
sigrok-cli doesn't support setting the two loglevels indepen- | |||
dently. The higher the number, the more debug output will be | |||
printed. Valid loglevels are: | |||
0 None | |||
1 Error | |||
2 Warnings | |||
3 Informational | |||
4 Debug | |||
5 Spew | |||
--show | |||
Show information about the selected option. For example, to see | |||
options for a connected fx2lafw device: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --show | |||
In order to properly get device options for your hardware, some | |||
drivers might need a serial port specified: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 --show | |||
This also works for protocol decoders, input modules and output | |||
modules: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --protocol-decoders i2c --show | |||
$ sigrok-cli --input-format csv --show | |||
$ sigrok-cli --output-format bits --show | |||
--scan Scan for devices that can be detected automatically. | |||
Example: | |||
$ sigrok-cli --scan | |||
The following devices were found: | |||
demo - Demo device with 12 channels: D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A0 | |||
A1 A2 A3 | |||
fx2lafw:conn=3.26 - CWAV USBee SX with 8 channels: 0 1 2 3 4 5 | |||
6 7 | |||
However, not all devices are auto-detectable (e.g. serial port | |||
based ones). For those you'll have to provide a conn option, | |||
see above. | |||
$ sigrok-cli --driver digitek-dt4000zc:conn=/dev/ttyUSB0 --scan | |||
The following devices were found: | |||
Digitek DT4000ZC with 1 channel: P1 | |||
--time <ms> | |||
Sample for <ms> milliseconds, then quit. | |||
You can optionally follow the number by s to specify the time to | |||
sample in seconds. | |||
For example, --time 2s will sample for two seconds. | |||
--samples <numsamples> | |||
Acquire <numsamples> samples, then quit. | |||
You can optionally follow the number by k, m, or g to specify | |||
the number of samples in kilosamples, megasamples, or gigasam- | |||
ples, respectively. | |||
For example, --samples 3m will acquire 3000000 samples. | |||
--frames <numframes> | |||
Acquire <numframes> frames, then quit. | |||
--continuous | |||
Sample continuously until stopped. Not all devices support this. | |||
--get <variable> | |||
Get the value of <variable> from the specified device and print | |||
it. | |||
--set Set one or more variables specified with the --config option, | |||
without doing any acquisition. | |||
EXAMPLES | |||
In order to get exactly 100 samples from the connected fx2lafw-sup- | |||
ported logic analyzer hardware, run the following command: | |||
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --samples 100 | |||
If you want to sample data for 3 seconds (3000 ms), use: | |||
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --time 3000 | |||
Alternatively, you can also use: | |||
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --time 3s | |||
To capture data from the first 4 channels using the Openbench Logic | |||
Sniffer lasting 100ms at 10 MHz starting at the trigger condition | |||
0:high, 1:rising, 2:low, 3:high, use: | |||
sigrok-cli --driver ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 --config samplerate=10m \ | |||
--output-format bits --channels 0-3 --wait-trigger \ | |||
--triggers 0=1,1=r,2=0,3=1 --time 100 | |||
To turn on internal logging on a Lascar EL-USB series device: | |||
sigrok-cli --driver lascar-el-usb:conn=10c4.0002 \ | |||
--config datalog=on --set | |||
EXIT STATUS | |||
sigrok-cli exits with 0 on success, 1 on most failures. | |||
SEE ALSO | |||
pulseview(1) | |||
BUGS | |||
Please report any bugs via Bugzilla (http://sigrok.org/bugzilla) or on | |||
the sigrok-devel mailing list (sigrok-devel@lists.souceforge.net). | |||
LICENSE | |||
sigrok-cli is covered by the GNU General Public License (GPL). Some | |||
portions are licensed under the "GPL v2 or later", some under "GPL v3 | |||
or later". | |||
AUTHORS | |||
Please see the individual source code files. | |||
This manual page was written by Uwe Hermann <uwe@hermann-uwe.de>. It | |||
is licensed under the terms of the GNU GPL (version 2 or later). | |||
October 22, 2018 SIGROK-CLI(1) | |||
</pre> | |||
</div> | |||
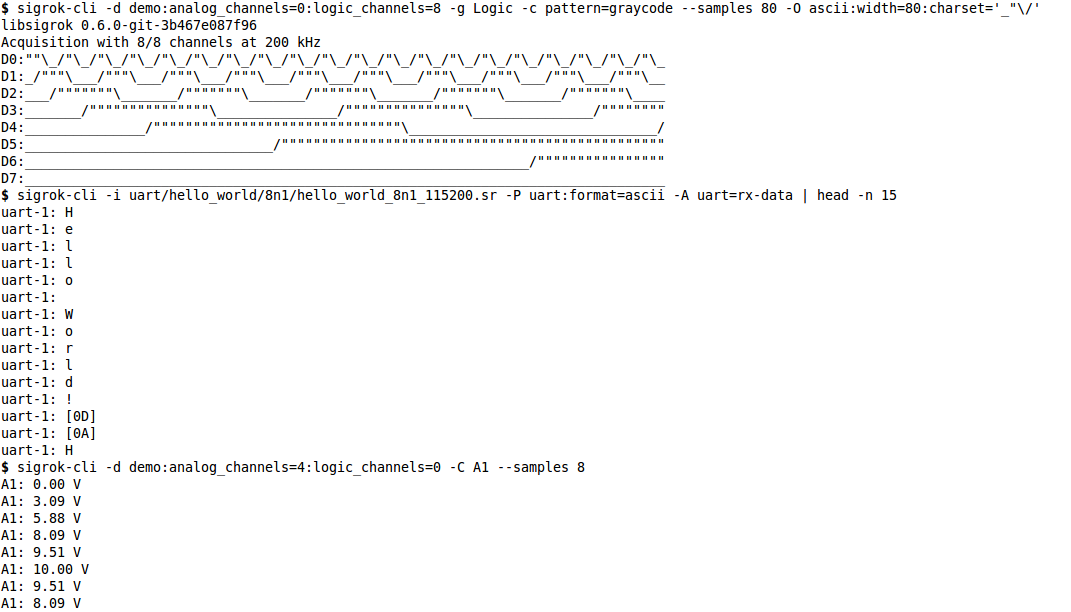
== Screenshots == | |||
=== sigrok-cli in action: logic data, decoder output, analog data === | |||
[[File:Sigrok-cli-screenshot-1.png]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:09, 7 July 2023
sigrok-cli (sometimes abbreviated as "cli") is a command-line frontend for sigrok.
It is licensed under the terms of the GNU GPL, version 3 or later.
Getting the code
$ git clone git://sigrok.org/sigrok-cli
You can also browse the source code via gitweb.
Distribution packages
See Downloads.
Building from source
See Building.
Usage tips
It is recommended to capture the data first and process them later. sigrok-cli is single-threaded application and too much load will overwhelm it resulting in early termination. For capturing, use binary output format (especially for high sample-rates). This is because other formats pose too big overhead.
$ sigrok-cli --driver saleae-logic-pro --channels 0=Vcc,1=CS,2=MISO,3=MOSI,4=CLK --output-file <file>.bin --output-format binary --config samplerate=50m --continuous
Even better, consider to use a buffer instead of direct write (even on SSD) and also compression.
$ sigrok-cli --driver saleae-logic-pro --channels 0=Vcc,1=CS,2=MISO,3=MOSI,4=CLK --output-format binary --config samplerate=50m --continuous | mbuffer | lz4 | pv > data.lz4q
Manpage
SIGROK-CLI(1) General Commands Manual SIGROK-CLI(1)
NAME
sigrok-cli - Command-line client for the sigrok software
SYNOPSIS
sigrok-cli [OPTIONS] [COMMAND]
DESCRIPTION
sigrok-cli is a cross-platform command line utility for the sigrok
software.
It cannot display graphical output, but is still sufficient to run
through the whole process of hardware initialization, acquisition, pro-
tocol decoding and saving the session.
It is useful for running on remote or embedded systems, netbooks, PDAs,
and for various other use-cases. It can display samples on standard
output or save them in various file formats.
OPTIONS
-h, --help
Show a help text and exit.
-V, --version
Show sigrok-cli version and the versions of libraries used.
-L, --list-supported
Show information about supported hardware drivers, input file
formats, output file formats, and protocol decoders.
-d, --driver <drivername>
A driver must always be selected (unless doing a global scan).
Use the -L (--list-supported) option to get a list of available
drivers.
Drivers can take options, in the form key=value separated by
colons.
Drivers communicating with hardware via a serial port always
need the port specified as the conn option. For example, to use
the Openbench Logic Sniffer:
$ sigrok-cli --driver=ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 [...]
Some USB devices don't use a unique VendorID/ProductID combina-
tion, and thus need that specified as well. This also uses the
conn option, using either VendorID.ProductID or bus.address:
USB VendorID.ProductID example:
$ sigrok-cli --driver=uni-t-ut61e:conn=1a86.e008 [...]
USB bus.address example:
$ sigrok-cli --driver=uni-t-ut61e:conn=4.6 [...]
-c, --config <deviceoption>
A colon-separated list of device options, where each option
takes the form key=value. For example, to set the samplerate to
1MHz on a device supported by the fx2lafw driver, you might
specify
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1m [...]
Samplerate is an option common to most logic analyzers. The
argument specifies the samplerate in Hz. You can also specify
the samplerate in kHz, MHz or GHz. The following are all equiv-
alent:
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1000000 [...]
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config samplerate=1m [...]
$ sigrok-cli -d fx2lafw --config "samplerate=1 MHz" [...]
-i, --input-file <filename>
Load input from a file instead of a hardware device. You can
specify "-" to use stdin as input. If the --input-format option
is not supplied, sigrok-cli attempts to autodetect the file for-
mat of the input file.
Example for loading a sigrok session file:
$ sigrok-cli -i example.sr [...]
Example for loading a WAV file (autodetection of input format):
$ sigrok-cli -i example.wav [...]
Example for loading a VCD file from stdin (autodetection of
input format):
$ cat example.vcd | sigrok-cli -i - [...]
-I, --input-format <format>
When loading an input file, assume it's in the specified format.
If this option is not supplied (in addition to --input-file),
sigrok-cli attempts to autodetect the file format of the input
file. Use the -L (--list-supported) option to see a list of
available input formats.
The format name may optionally be followed by a colon-separated
list of options, where each option takes the form key=value.
Example for loading a binary file with options:
$ sigrok-cli -i example.bin
-I binary:numchannels=4:samplerate=1mhz [...]
-o, --output-file <filename>
Save output to a file instead of writing it to stdout. The
default format used when saving is the sigrok session file for-
mat. This can be changed with the --output-format option.
Example for saving data in the sigrok session format:
$ sigrok-cli [...] -o example.sr
-O, --output-format <format>
Set the output format to use. Use the -L (--list-supported)
option to see a list of available output formats.
The format name may optionally be followed by a colon-separated
list of options, where each option takes the form key=value.
For example, the bits or hex formats, for an ASCII bit or ASCII
hexadecimal display, can take a "width" option, specifying the
number of samples (in bits) to display per line. Thus -O
hex:width=128 will display 128 bits per line, in hexadecimal:
0:ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff
1:ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00 ff00
The lines always start with the channel number (or name, if
defined), followed by a colon. If no format is specified, it
defaults to bits:width=64, like this:
0:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
1:11111111 00000000 11111111 00000000 [...]
Example for saving data in the CSV format with options:
$ sigrok-cli [...] -o example.csv -O csv:dedup:header=false
Notice that boolean options are true when no value gets speci-
fied.
-C, --channels <channellist>
A comma-separated list of channels to be used in the session.
Note that sigrok always names the channels according to how
they're shown on the enclosure of the hardware. If your logic
analyzer numbers the channels 0-15, that's how you must specify
them with this option. An oscilloscope's channels would gener-
ally be referred to as "CH1", "CH2", and so on. Use the --show
option to see a list of channel names for your device.
The default is to use all the channels available on a device.
You can name a channel like this: 1=CLK. A range of channels
can also be given, in the form 1-5.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --samples 100
--channels 1=CLK,2-4,7
CLK:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
2:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
3:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
4:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
7:11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 [...]
The comma-separated list is processed from left to right, i.e.
items farther to the right override previous items. For example
1=CS,CS=MISO will set the name of channel 1 to MISO.
-g, --channel-group <channel group>
Specify the channel group to operate on. Some devices organize
channels into groups, the settings of which can only be changed
as a group. The list of channel groups, if any, is displayed
with the --show command.
Examples:
$ sigrok-cli -g CH1 [...]
$ sigrok-cli -d demo -g Logic -c pattern=graycode [...]
-t, --triggers <triggerlist>
A comma-separated list of triggers to use, of the form <chan-
nel>=<trigger>. You can use the name or number of the channel,
and the trigger itself is a series of characters:
0 or 1: A low or high value on the pin.
r or f: A rising or falling value on the pin. An r effectively
corresponds to 01.
e: Any kind of change on a pin (either a rising or a falling
edge).
Not every device supports all of these trigger types. Use the
--show command to see which triggers your device supports.
-w, --wait-trigger
Don't output any sample data (even if it's actually received
from the hardware) before the trigger condition is met. In other
words, do not output any pre-trigger data. This option is useful
if you don't care about the data that came before the trigger
(but the hardware delivers this data to sigrok nonetheless).
-P, --protocol-decoders <list>
This option allows the user to specify a comma-separated list of
protocol decoders to be used in this session. The decoders are
specified by their ID, as shown in the -L (--list-supported)
output.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c
Each protocol decoder can optionally be followed by a colon-sep-
arated list of options, where each option takes the form
key=value.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr>
-P uart:baudrate=115200:parity_type=odd
The list of supported options depends entirely on the protocol
decoder. Every protocol decoder has different options it sup-
ports.
Any "options" specified for a protocol decoder which are not
actually supported options, will be interpreted as being channel
name/number assignments.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr>
-P spi:wordsize=9:miso=1:mosi=5:clk=3:cs=0
In this example, wordsize is an option supported by the spi pro-
tocol decoder. Additionally, the user tells sigrok to decode the
SPI protocol using channel 1 as MISO signal for SPI, channel 5
as MOSI, channel 3 as CLK, and channel 0 as CS# signal.
Notice that the sigrok-cli application does not support "name
matching". Instead it's assumed that the traces in the input
stream match the order of the decoder's input signals, or that
users explicitly specify the input channel to decoder signal
mapping.
When multiple decoders are specified in the same -P option, they
will be stacked on top of each other in the specified order.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,eeprom24xx
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P uart:baudrate=31250,midi
When multiple -P options are specified, each of them creates one
decoder stack, which executes in parallel to other decoder
stacks.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P uart:tx=D0:rx=D1 -P timing:data=D2
-A, --protocol-decoder-annotations <annotations>
By default, all annotation output of all protocol decoders is
shown. With this option a specific decoder's annotations can be
selected for display, by specifying the decoder ID:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid -A i2c
If a protocol decoder has multiple annotation classes, you can
also specify which one of them to show by specifying its short
description like this:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid
-A i2c=data-read
Select multiple annotation classes by separating them with a
colon:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid
-A i2c=data-read:data-write
You can also select multiple protocol decoders, with an optional
selected annotation class each, by separating them with commas:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -P i2c,i2cfilter,edid
-A i2c=data-read:data-write,edid
-M, --protocol-decoder-meta <pdname>
When given, show protocol decoder meta output instead of annota-
tions. The argument is the name of the decoder whose meta out-
put to show.
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -M i2c
Not every decoder generates meta output.
-B, --protocol-decoder-binary <binaryspec>
When given, decoder "raw" data of various kinds is written to
stdout instead of annotations (this could be raw binary UART/SPI
bytes, or WAV files, PCAP files, PNG files, or anything else;
this is entirely dependent on the decoder and what kinds of
binary output make sense for that decoder).
No other information is printed to stdout, so this is suitable
for piping into other programs or saving to a file.
Protocol decoders that support binary output publish a list of
binary classes, for example the UART decoder might have "TX" and
"RX". To select TX for output, the argument to this option would
be:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -B uart=tx
If only the protocol decoder is specified, without binary class,
all classes are written to stdout:
$ sigrok-cli -i <file.sr> -B uart
(this is only useful in rare cases, generally you would specify
a certain binary class you're interested in)
Not every decoder generates binary output.
--protocol-decoder-samplenum
When given, decoder annotations will include sample numbers,
too. This allows consumers to receive machine readable timing
information.
-l, --loglevel <level>
Set the libsigrok and libsigrokdecode loglevel. At the moment
sigrok-cli doesn't support setting the two loglevels indepen-
dently. The higher the number, the more debug output will be
printed. Valid loglevels are:
0 None
1 Error
2 Warnings
3 Informational
4 Debug
5 Spew
--show
Show information about the selected option. For example, to see
options for a connected fx2lafw device:
$ sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --show
In order to properly get device options for your hardware, some
drivers might need a serial port specified:
$ sigrok-cli --driver ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 --show
This also works for protocol decoders, input modules and output
modules:
$ sigrok-cli --protocol-decoders i2c --show
$ sigrok-cli --input-format csv --show
$ sigrok-cli --output-format bits --show
--scan Scan for devices that can be detected automatically.
Example:
$ sigrok-cli --scan
The following devices were found:
demo - Demo device with 12 channels: D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A0
A1 A2 A3
fx2lafw:conn=3.26 - CWAV USBee SX with 8 channels: 0 1 2 3 4 5
6 7
However, not all devices are auto-detectable (e.g. serial port
based ones). For those you'll have to provide a conn option,
see above.
$ sigrok-cli --driver digitek-dt4000zc:conn=/dev/ttyUSB0 --scan
The following devices were found:
Digitek DT4000ZC with 1 channel: P1
--time <ms>
Sample for <ms> milliseconds, then quit.
You can optionally follow the number by s to specify the time to
sample in seconds.
For example, --time 2s will sample for two seconds.
--samples <numsamples>
Acquire <numsamples> samples, then quit.
You can optionally follow the number by k, m, or g to specify
the number of samples in kilosamples, megasamples, or gigasam-
ples, respectively.
For example, --samples 3m will acquire 3000000 samples.
--frames <numframes>
Acquire <numframes> frames, then quit.
--continuous
Sample continuously until stopped. Not all devices support this.
--get <variable>
Get the value of <variable> from the specified device and print
it.
--set Set one or more variables specified with the --config option,
without doing any acquisition.
EXAMPLES
In order to get exactly 100 samples from the connected fx2lafw-sup-
ported logic analyzer hardware, run the following command:
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --samples 100
If you want to sample data for 3 seconds (3000 ms), use:
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --time 3000
Alternatively, you can also use:
sigrok-cli --driver fx2lafw --time 3s
To capture data from the first 4 channels using the Openbench Logic
Sniffer lasting 100ms at 10 MHz starting at the trigger condition
0:high, 1:rising, 2:low, 3:high, use:
sigrok-cli --driver ols:conn=/dev/ttyACM0 --config samplerate=10m \
--output-format bits --channels 0-3 --wait-trigger \
--triggers 0=1,1=r,2=0,3=1 --time 100
To turn on internal logging on a Lascar EL-USB series device:
sigrok-cli --driver lascar-el-usb:conn=10c4.0002 \
--config datalog=on --set
EXIT STATUS
sigrok-cli exits with 0 on success, 1 on most failures.
SEE ALSO
pulseview(1)
BUGS
Please report any bugs via Bugzilla (http://sigrok.org/bugzilla) or on
the sigrok-devel mailing list (sigrok-devel@lists.souceforge.net).
LICENSE
sigrok-cli is covered by the GNU General Public License (GPL). Some
portions are licensed under the "GPL v2 or later", some under "GPL v3
or later".
AUTHORS
Please see the individual source code files.
This manual page was written by Uwe Hermann <uwe@hermann-uwe.de>. It
is licensed under the terms of the GNU GPL (version 2 or later).
October 22, 2018 SIGROK-CLI(1)